Sunlight Hours
We will discuss how skin color and planet-science affects our risks of skin cancer, and Vitamin D deficiency.
These two topic are very related. One is too much sun for some; the other is too little litle sunlight for others.
(my apologies for the different sizes of the maps, I can only borrow them, not create them)
In these maps, red means warmer, blue means cooler.
Underexposure can create VitD (Vitamin D) deficiency, which affects many parts of our health, including COVID-risk.
Overexposure to sunlight, gives people a higher risk of skin cancer.
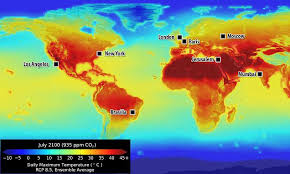
The top photo shows the average temperatures of the earth through out the year.
Notice it is darkest red in the middle, where the equator is located, and morphs into deep blues at both poles.
This is expected.
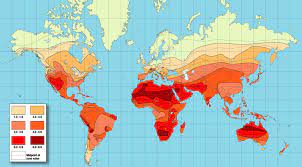
The second photo shows the average strength of sunlight in different parts of the world.
This color shot is far different from the first photo.
Shouldn't all land-areas near the equators have the same strength of sun? No, not at all. This is part of the mystery.
Look at the third map. The green areas receive more rain, and have more plant-life.
The brown areas are desert-y areas that get less rain.
And notice that the equator may be the greenest 40 degree-strip on the planet. And it is alsothe warmest.
So shouldn't the equator, being the warmest, also be desert?
No. Warm air on the equator vaporizes more water, which gives more rain.
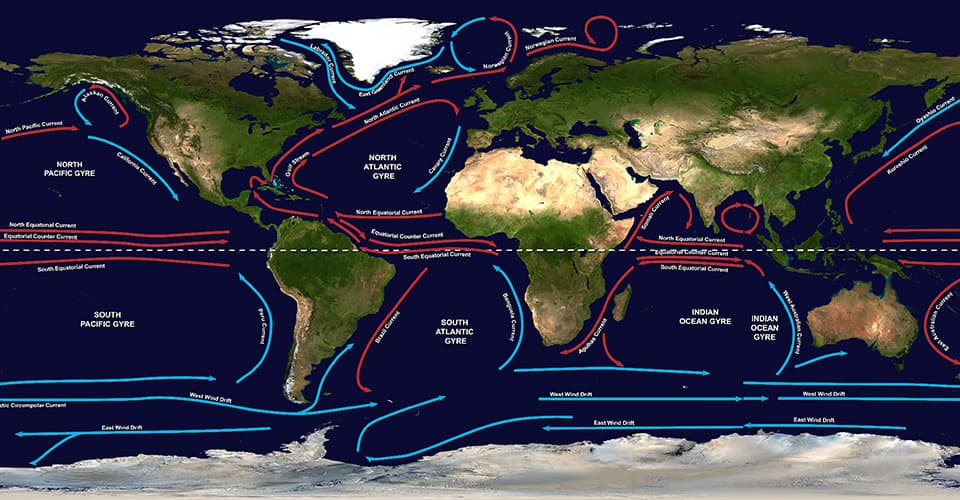
Gyres, sea and wind currents tell a story of a different, mysterious kind.
Red currents bring rain, blue currents bring drought.
More info:
Ocean currents circle between continents, like water inside a toilet bowl. The biggest circles are called 'ocean gyres'.
They are due partly to the 'coriolus effect'. Our huge planet, making one full turn once a day, is like a car taking a turn.
Anything not fastened down, tends to move around, especially the water in the oceans and the air in the atmosphere.
The coriolus effect makes a lot of wind and waves, and bounce off the continents.
When winds moves over warm equatorial water, the air absorbs water.
Some of that air travels inland, then rains when the air cools off enough that the air can no longer hold the water.
Warm air on the equator holds more warm water, than cool air can hold cool water.
The green in the third map shows where it rains the most.
Also, the part of the earth that doesn't get many clouds, gets hotter during the day, because clouds actually reflect sunlight back into space.
*************************
Next, 'Ancestral Vitamin D Traits'.
Every person gains VitD partly through exposure to sunlight, according to their skin color, and the density of the sunlight in their current location. VitD is is a necessary vitiamin, and helps us resist attacks from things like COVID.
The darker the skin of the person, the more sunlight needed to make their VitD.
Now let's apply the math from map #2, keeping in mind the role of sunlight, VitD and COVID...
There is an average of 3664 hours of sunlight in Khartoum, Sudan, out of a possible 4383 hours, or 10:01 hours sunlight per day.
There is an average of 2592 hours in sunlight Portland, Maine, out of a possible 4383 hours, or 7:05 hours sunlight per day.
Can you see how immigration can affect personal health?
And sunlight is a double-edge sword. Not enough sunshine...brings the possiblity of COVID, rickets, etc.
And too much sunshine, as in a Finn moving to Australia, brings the possibility of skin cancer.
See what maps can do for us?
Sometimes, maps give us treasure without filling our pockets.
Eric J. Rose
middlegrademysteries.com
photo 1: dailymail.co.uk ave temps
photo 2: pinterest.com sunlight hours
photo 3: oceanservice.noaa.gov gyres